
7 Key Tenets of Zero Trust Architecture
Being in the cybersecurity domain often gets overwhelming with new technologies popping up every other day. The same has been the case with the buzz surrounding concepts like zero trust. While there’s no shortage of definitions floating around, the National Institute of Standards and Technology, or NIST, offers a practical framework with its core elements of zero trust.
In their publication, NIST SP 800-207, they outline seven key tenets that form the foundation of zero trust architecture. These principles provide a clear roadmap for organizations looking to boost their cybersecurity posture. While understanding the principles is essential, it’s equally important to grasp the practical implementation of zero trust controls within an organization.
Let’s learn more about these principles and explore how organizations can translate theory into action for a successful zero trust architecture.
What are the 7 Key Tenets of Zero Trust Architecture?
The Zero Trust Architecture is defined by seven key tenets, each essential for its effective inclusion in a company’s cybersecurity infrastructure. NIST SP 800-207 serves as a beacon for these tenets as it offers practical guidance for their real-world application. These seven key tenets are:
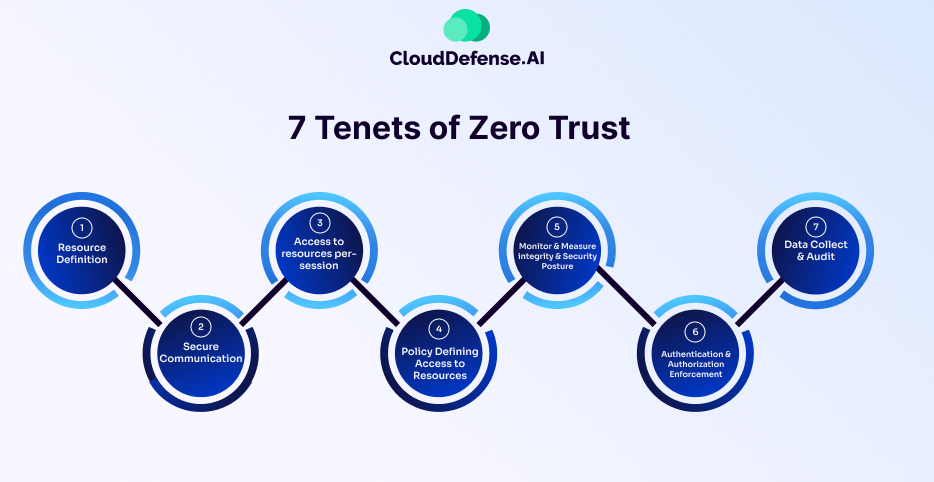
All data sources and computing services are considered resources
In the past, people used to mainly think about protecting computers and servers. But now, the rise of IoT devices and cloud services requires us to broaden our thinking. It's not just about computers anymore, it's about all kinds of gadgets and online services that connect to your networks. To keep these devices safe, you need to have really strong ways of checking who's trying to access them and only giving them the least amount of access they need to get their job done.
All communication is secured regardless of network location
Zero Trust Network Access, or ZTNA, is implemented in Zero Trust infrastructures. ZTNA requires you to have a strict "permission only" rule for accessing resources. Instead of assuming everyone can access everything by default, it only allows access to specific resources when explicitly granted. This is super important nowadays because lots of employees work remotely with varying types of devices. With ZTNA, we can control who gets access to what, even if they're not in the office, helping to keep our resources safe from unauthorized access.
Access to individual enterprise resources is granted on a per-session basis
Continuous evaluation of user trustworthiness is maintained by always checking to make sure people are who they say they are and that they're only getting access to what they really need. This way, you can avoid giving anyone more access than necessary, which could lead to security threats if someone's credentials get compromised. By checking each time someone tries to access something, you prevent access privileges from being automatically passed on from one session to another or from one resource to another. This helps keep your systems secure and reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
Access to resources is determined by a dynamic policy
Access policies require you to consider different factors, like who the user is, the health of their device, and where they're connecting from. These policies aren't set in stone—they change based on what's happening in real-time. So, if something unusual is detected, like a device acting strangely or someone trying to log in from a suspicious location, the policies can adapt to make sure everything stays secure. This flexibility helps you stay ahead of potential threats and keeps your systems protected, no matter what changes occur.
The enterprise monitors and measures the integrity and security posture of all owned and associated assets
Continuous monitoring is required to keep a close eye on all the devices connected to your organization's IT systems. You need to make sure they're safe and set up correctly. If you notice any issues, like a missing security update or a potential vulnerability, fix them right away. This proactive approach would help you stay on top of any potential risks and keep our systems running smoothly and securely.
All resource authentication and authorization are dynamic and strictly enforced before access is allowed
Access decisions are made in real-time and strictly enforced, meaning you don't rely on past permissions or assumptions. Each time someone tries to access something, you carefully evaluate a bunch of different factors to decide if they should be allowed in. This includes things like who they are, what device they're using, and where they're trying to access from. By looking at all these factors every time, you make sure that only the right people get access to the right things, reducing the risk of any security breaches.
The enterprise collects as much information as possible about the current state of assets, network infrastructure, and communications and uses it to improve its security posture
Data collection and analysis are vital for making better decisions and keeping your security strong. By keeping an eye on the state of your assets and how your network is communicating, you can learn a lot about potential risks and threats. This information helps you update your access policies and security measures to stay ahead of any new dangers. Being able to adapt quickly like this allows you to keep your organization safe in this treacherous technological environment.
To Sum Up
Zero Trust Architecture focuses on continuous verification, least privilege access, and segmentation to strengthen cybersecurity. While tools aid implementation, ZTA isn’t a quick fix—it’s a journey requiring custom-made strategies and maturity stages. The NSA recommends a phased approach that needs companies to assess current practices, identify gaps, and develop a plan. Success demands a holistic view, integrating people, processes, and technology.
Successful implementation of Zero Trust Architecture also requires companies to have strong policies in place that are customized according to their needs. This can be quite sophisticated for companies that are new to this domain of cyber security. To assist you with that CloudDefense.AI has created an open source AWS Policy Generator API that harnesses AWS Cloud Trail logs to generate IAM policies with the principle of least privilege. Download the repo here to witness the power of AWSZeroTrustPolicy API!
